-
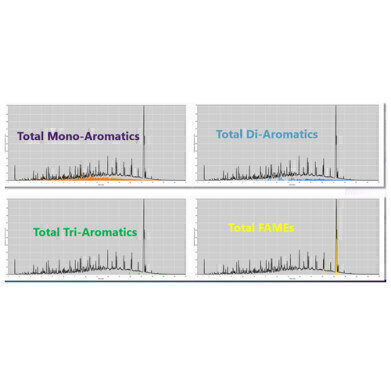 Figure 1. The new GC-VUV diesel method measures total mono-aromatics, total di-aromatics, total tri-aromatics and total FAMEs (Fatty Acid Methyl Esters).
Figure 1. The new GC-VUV diesel method measures total mono-aromatics, total di-aromatics, total tri-aromatics and total FAMEs (Fatty Acid Methyl Esters). -

Analytical instrumentation
Newly Proposed ASTM Method for Determination of Aromatics in Diesel
Oct 12 2020
"It's only a few more carbon numbers" – a few small, harmless words that with the successful adoption of ASTM D8267 into the international jet fuel specification ASTM D1655, spawned the development of a similar GC-VUV method for diesel analysis. The objective of VUV Analytics’ new diesel method was to seamlessly run it in conjunction with the ASTM D8267 jet fuel method, which in turn is run on the same hardware as the GC-VUV ASTM D8071 gasoline method. Development of the diesel method was accomplished by extending the D8267 final oven temperature hold time by about 10 minutes which extended the applicable boiling range from 356°C (heneicosane) to 450°C (triacontane). The expanded boiling range now captures the final boiling point of diesel, similar mid-distillates, renewable diesels, and fatty acid methyl esters (FAME) (Figure 1). Three ring aromatics elute in this extended boiling point range thus allowing the quantitation of a tri+ aromatics group in addition to the monoaromatics and diaromatics.
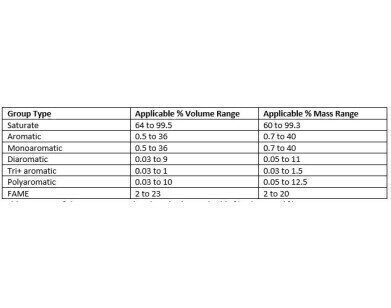
The scope of the method is shown in Table 1.
The applicable ranges of the group types and final precision will ultimately be defined by an interlaboratory study that is currently underway.
Method protocols include standard gas chromatograph conditions as well as optimising instrument-to-instrument response for naphthalene, splitter linearity checks and target group type tolerance limits for validation mixtures. The result is a robust method with precision that is shown to be 5X to 10X better than alternate aromatics methods.
The use of FAMEs from various feedstocks in diesel fuel is mandated in many parts of the world and retail diesel containing up to 5% FAME can be un-labelled at the pump. Therefore, having a single analysis that covers both aromatics and FAMEs is very beneficial. It’s worth noting that FAMEs elute from the non-polar column used in our diesel analysis and do not interfere with the measurement of aromatics.
Total aromatics and polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are also regulated in many diesel fuel specifications since NOx emissions are lowered by a reduction of total aromatics. Additionally, particulate matter and direct PAH emissions are correlated to PAH concentration, therefore having an accurate way to measure these values is vital.
The new GC-VUV diesel method provides a fast, easy and accurate measurement of these important diesel fuel parameters. The method with interim precision is currently in the final phase of ASTM balloting. The new ASTM method is used in conjunction with new VUV extended library and diesel software application.
Fortunately, for users of our VUV Analyzer™ Platform for Fuels, the GC-VUV diesel method can be run on the same system as our gasoline and jet fuel methods with no changes in hardware or setup, making it possible to have an all-in-one system for fuels analysis.
Digital Edition
PIN 26.1 Feb/Mar 2025
March 2025
Analytical Instrumentation - Elemental Analysis for Quality and Process Control at Refineries, for Lubricants and Wear Metals in Engine Oils - Synthetic Lubricants: New Developments - Scaling...
View all digital editions
Events
Apr 08 2025 Birmingham, UK
Apr 08 2025 Kielce, Poland
Apr 08 2025 Ravenna, Italy
Apr 08 2025 Southampton, UK
Apr 08 2025 London, UK